Re-imagining requirements management for safety-critical projects

Project teams face a host of challenges when developing semiconductors compliant to a safety critical market. Whether that’s ISO 26262 (Automotive), DO-254 (Avionics), IEC 61508 (Industrial), or others, project teams must do more and deliver more to achieve compliance and deliver safe products to market.
In the context of ISO 26262, much of the discussion in recent years has been on challenges addressing run time failures (random failures). But lately, the volume of chatter discussing the challenges of executing a requirements-driven lifecycle to deliver bug and defect free silicon is growing. Frankly, this isn’t surprising when looking at the latest Wilson Research Survey data. The data suggests a convergence of scenarios ultimately driving an exponential growth in design complexity. This includes:
- 58% of designs are 10M gates or greater
- 52% of designs contain at least two processing cores
- 34% of designs contain an AI accelerator
- 80% of automotive designs contain security features
- 86% of designs have active power management
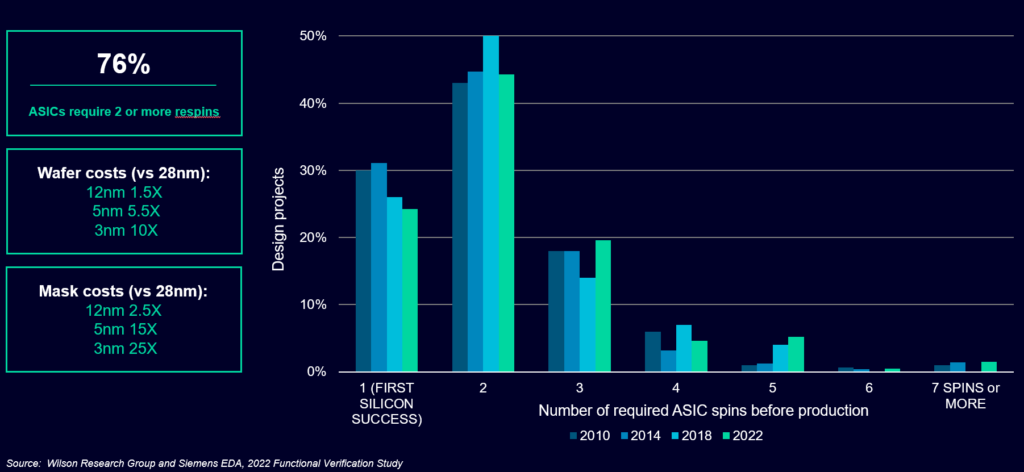
All of this supports the larger data point that 76% of ASICs will require two or more respins, a concerning trend given rising fabrication costs. As complexity rises, the probability of first silicon success lessens unless project teams evolve with new methodologies and automation, including how project teams manage requirements.
Challenges in Requirements Management
Requirements driven development is a foundational component of any safety critical lifecycle, including ISO 26262, the state-of-the-art standard guiding safety in the development of automotive electronic devices. At face value, requirements seem like a very straight forward concept.
- Project teams write requirements
- Requirements are implemented into the product
- The product is tested to ensure the requirements have been met
Simple enough, right? Feedback from industry practitioners paint a much different picture. The ground truth is that there are a whole host of challenges that project teams face, and many of those challenges are rooted in inadequate requirements practices.
Fortunately, ISO 26262 has provided some guidance in managing requirements, an example being ISO 26262:2018-8 Clause 6. The guidance covers requirement notation, attributes of a safety requirement, and the management of requirements.
But even with this guidance, project teams still face a host of challenges, including:
- Enforcing good requirement structures to make certain they are unambiguous, comprehensible, atomic, feasible, and verifiable
- Configuring workflows that support requirement reviews, approvals, impact analysis, and more
- Capturing and decomposing requirements both within a project and across the supply chain
- Tracing requirements to lifecycle artifacts to prove the requirements are realized and verified
Traceability is a core component of a requirements-driven lifecycle and links a requirement to the implementation and verification evidence. Project teams must establish traceability across various threads.
The ISO 26262 standard went so far as to recommend the use of requirements management tools.
In order to support the management of safety requirements, the use of suitable requirements management tools is recommended.
ISO 26262:2018-8 Clause 6.2
To counter challenges project teams face managing requirements, Siemens developed an integrated suite of solutions that advances existing requirements management practices and automates integration with silicon development activities.
Establishing the Digital Thread with Siemens EDA
Siemens Digital Industries Software offers a suite of products tailored to supporting requirements driven flows. These products underscore the Siemens Xcelerator open ecosystem mindset by providing APIs and industry standard interfaces, and therefore offer maximum flexibility in establishing traceability across diverse toolchains. In addition to open interface support, Siemens has implemented native integration between Siemens Polarion™ and Questa™ Verification IQ.
Siemens Polarion is a complete application lifecycle management solution providing a suite of integrated application lifecycle management (ALM) modules across project management, requirements management, change and configuration management, quality management, and more.

Questa Verification IQ is Siemens EDA data-driven verification solution leveraging analytics and collaborative web-based technologies to deliver a new paradigm in how semiconductors are designed and verified. Verification IQ is ISO 26262 certified by TÜV Saar and pre-qualified for use within ASIL-D projects.
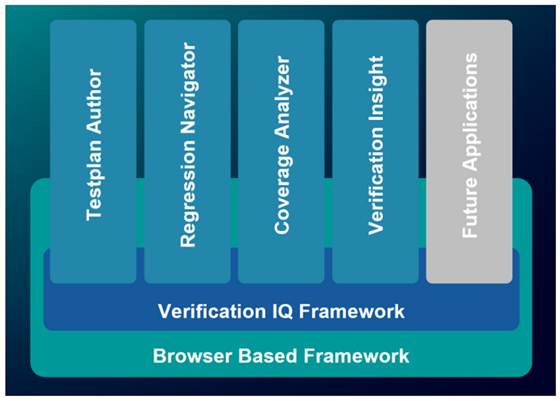
Native integration between Polarion and Questa Verification IQ provides dynamic real-time linking between requirements and verification data. Once mapped, requirements are directly traced to the verification artifacts that prove that the requirement was adequately tested. This automation provides three key benefits:
- Takes the engineer out of the loop in managing requirement relationships
- Eliminates situations where requirement analysis is incorrect due to stale lifecycle data
- Enables efficient triage of incomplete requirements
Leveraging industry standard interfaces, users can dynamically view the verification artifacts from within the requirements management environment or requirements from within the Verification IQ environment. Up to date visibility is guaranteed, and the complexities surrounding data synchronization are automated behind the scenes.
Once linked, stakeholders (assessors, project leads, safety managers, etc.) can view in real time the verification status for each requirement within their preferred working environment.

Conclusion
Project teams continue to battle against three opposing forces: rising silicon complexity, high cost of failure, and shortened development cycles. Further complicating matters is the need for efficient collaboration across disparate functions, geographies, and business units, as well as with external entities.
One area where operational inefficiencies exist is in how project teams manage lifecycle data within a requirements-driven workflow. Busy, overpopulated solution landscapes and traditional manual methods incur unacceptable levels of overhead and must be replaced by a solution that provides full collaborative, scalable, lifecycle management and verification management in a single system. Such a solution cuts overhead and complexity. Siemens is the leader in delivering a complete set of tailored, safety critical software solutions featuring native integrations between the lifecycle management and EDA worlds. If you’d like to learn more detail about how Siemens automation addresses requirements, traceability, and the management of lifecycle data, please read our full paper, Intelligent requirements traceability for ISO 26262.
Comments
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.


That was so great I loved that Information. It’s a very help full to everyone.